Prologue
- Digital financial services have become instrumental in enhancing financial inclusion by providing cost-effective, efficient, and secure access to financial products, bridging the gap for under- served populations.
- Microfinance institutions have provided over $124 billion in loans to low-income individuals and small businesses worldwide.
- Households with bank accounts are more likely to save, invest in education, and manage financial shocks better. Women remain less likely than men to have a bank account, particularly in low-income regions.
Introduction
Financial inclusion is the process of ensuring access to appropriate financial products and services for all individuals and businesses, particularly those in underserved and marginalized communities. This report examines the current state of financial inclusion, barriers to access, and strategies to enhance financial services for all. By analyzing successful initiatives worldwide, this study provides recommendations for policymakers, financial institutions, and technology providers to bridge the financial gap and promote economic empowerment.
Financial inclusion plays a crucial role in economic development by providing individuals and businesses with the tools needed to manage finances, save, invest, and mitigate financial risks. Despite significant progress, millions of people worldwide remain excluded from formal financial systems due to barriers such as geographical constraints, lack of financial literacy, and high costs of services.
The Importance of Financial Inclusion
Financial inclusion ensures that individuals and businesses can access affordable and useful financial products, such as savings accounts, credit, insurance, and payment systems. The benefits include:
- Economic Growth: Financial inclusion boosts economic growth by enabling more people to access financial services. It allows individuals and small businesses to save, invest, and expand. This leads to increased productivity and job creation. A well-financed population contributes to a stronger economy.
- Poverty Reduction: Access to financial services helps low-income individuals manage their money better. It enables them to save, invest in education, and build assets. Microloans and insurance protect against financial shocks. This reduces poverty and improves living standards.
- Empowerment of Women and Marginalized Groups: Financial inclusion gives women and marginalized communities access to banking, credit, and investment opportunities. It helps them start businesses, achieve financial independence, and improve their quality of life. This fosters gender equality and social development.
- Empowerment of Women and Marginalized Groups: Financial inclusion gives women and marginalized communities access to banking, credit, and investment opportunities. It helps them start businesses, achieve financial independence, and improve their quality of life. This fosters gender equality and social development.
- Encouraging Entrepreneurship: Access to credit and banking services enables entrepreneurs to start and grow businesses. It allows them to secure capital, manage cash flow, and expand operations. This creates more jobs and innovation. A thriving entrepreneurial ecosystem boosts economic resilience.
- Better Financial Security and Resilience: Financial inclusion helps individuals save for emergencies, invest in insurance, and manage risks. It reduces dependence on informal and high-cost lending sources. This creates financial stability and reduces vulnerability to economic shocks.
Financial Inclusion in India
Financial inclusion in India is crucial for economic growth, poverty reduction, and social empowerment. Government initiatives like Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) have expanded banking access, with over 500 million accounts opened. Increased digital payment adoption has further enhanced financial accessibility, bridging gaps between rural and urban populations. By providing access to credit, insurance, and savings, financial inclusion fosters entrepreneurship, strengthens financial security, and boosts overall economic stability, ensuring inclusive development.
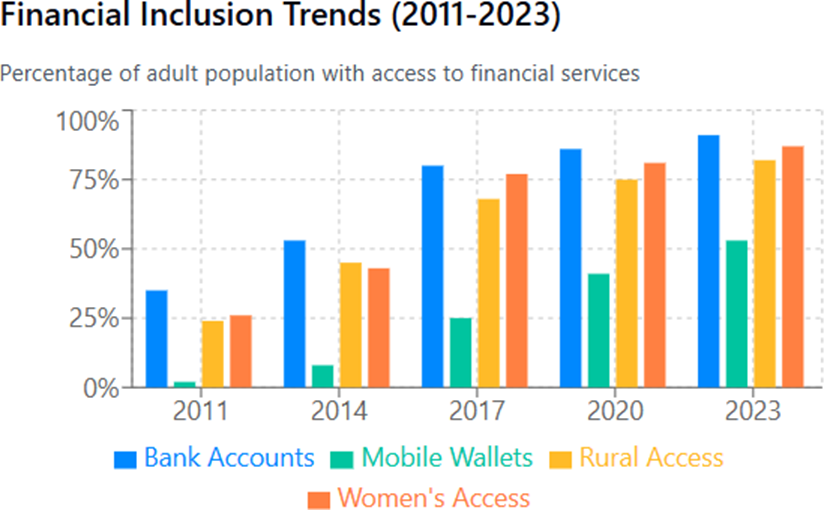
- Transformative Impact of PMJDY: Bank account ownership surged from 35% in 2011 to 80% by 2017 following the 2014 launch of Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana.
- Digital Revolution: Mobile wallet adoption saw the most dramatic growth, increasing 26x from 2% to 53% over the period, accelerated by demonetization in 2016 and UPI introduction.
- Closing Gender Gap: Women’s financial access grew from just 26% in 2011 to 87% in 2023, nearly eliminating the gender gap in basic financial services.
- Rural Inclusion: Rural access expanded significantly from 24% to 82%, though a 9% gap compared to the national average (91%) persists.
Strategies to Enhance Financial Inclusion
- Expanding Digital Banking and Payments: Digital banking, mobile wallets, and UPI (Unified Payments Interface) simplify access to financial services. They reduce the need for physical bank branches, making banking more accessible, especially in rural areas. Government initiatives like Aadhaar-linked banking help streamline transactions.
- Strengthening Financial Literacy Programs: Educating people about financial services, savings, credit management, and digital transactions empowers them to make informed decisions. Financial literacy programs in schools, workplaces, and rural communities can bridge the knowledge gap. This ensures responsible financial behavior and better financial security.
- Encouraging Microfinance and Small Loans: Microfinance institutions (MFIs) and self-help groups provide small loans to underserved communities. These funds help entrepreneurs, farmers, and small businesses grow. Low-interest microloans improve access to credit for those who lack collateral for traditional bank loans.
- Enhancing Banking Infrastructure in Rural Areas: Expanding bank branches, ATMs, and Business Correspondents (BCs) in remote locations ensures better access to financial services. Mobile banking vans and digital kiosks can further extend banking facilities. Strengthening rural banking networks reduces dependency on informal lending sources.
- Government Policies and Incentives: Policies like Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) and Direct Benefit Transfers (DBT) promote financial inclusion. Subsidies and incentives for banks to serve low-income customers encourage broader financial access. Regulatory support for fintech innovations further enhances financial reach.
- Encouraging Private Sector and Fintech Participation: Collaboration between banks, fintech companies, and telecom providers helps create innovative financial products. Mobile banking apps, AI-driven financial planning tools, and blockchain-based services improve efficiency. Private sector involvement boosts technological advancements and service delivery.
Financial Services Usage in India
The usage of financial services is essential for economic stability, individual security, and business growth. Access to banking, credit, insurance, and digital payments enables people to manage finances effectively, invest in opportunities, and safeguard against financial risks. Increased financial service usage fosters entrepreneurship, enhances savings, and promotes economic resilience. It also supports national development by driving formal economic participation and improving overall financial well-being.
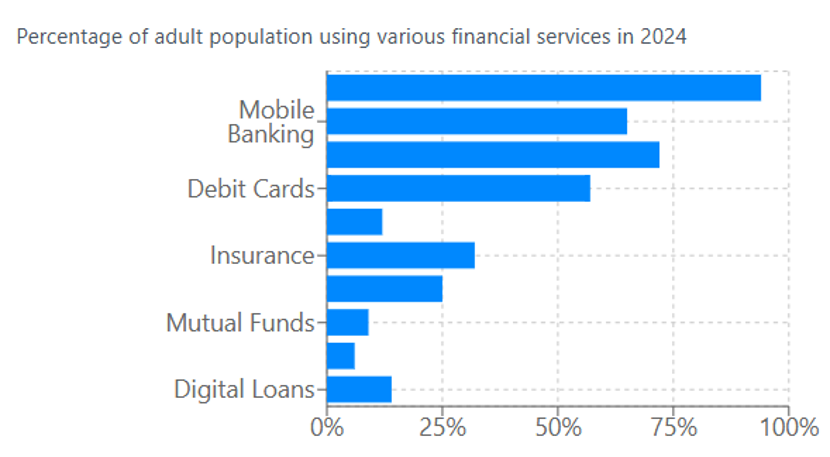
Key Observations:
- Digital Acceleration: UPI payments (72%) have surpassed debit card usage (57%), marking India’s shift to direct digital payments over card-based transactions.
- Mobile-First Adoption: Mobile banking (65%) has become the primary channel for financial services, reflecting smartphone penetration and simplified apps.
- Credit Gap: Despite high banking penetration (94%), credit card adoption remains low (12%), indicating continued barriers in formal credit access.
- Investment Participation: Combined investment products (mutual funds at 9% and stocks at 6%) show gradual growth but remain limited to urban and higher-income segments.
- Protection Services: Insurance adoption has increased to 32%, driven by simplified digital policies and government schemes, but significant protection gaps remain.
Urban vs. Rural Digital Payment Adoption
Urban areas have witnessed faster adoption of digital payments due to better internet connectivity, smartphone penetration, and financial literacy. Services like UPI, mobile wallets, and online banking are widely used for transactions, shopping, and bill payments. In contrast, rural adoption has been slower due to limited infrastructure, lower digital literacy, and cash dependence. However, government initiatives, fintech solutions, and mobile banking are gradually bridging the gap, making digital payments more accessible even in remote regions.
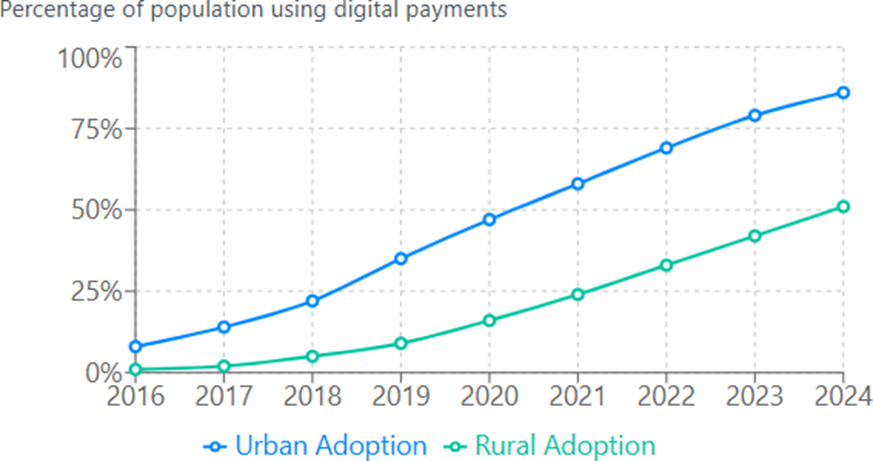
Key Observations:
- Narrowing Divide: The urban-rural adoption gap has decreased from 7x in 2016 (8% vs 1%) to 1.7x in 2024 (86% vs 51%), showing significant rural progress.
- Rural Acceleration: Rural adoption has grown at a faster percentage rate, with a 51x increase compared to urban’s 10.75x increase over the period.
- Infrastructure Impact: The correlation between rural internet penetration growth and digital payment adoption indicates infrastructure as a key enabler.
- Critical Mass: Rural adoption crossed 33% in 2022, creating the critical mass needed for wider ecosystem development and merchant participation.
- Ongoing Challenge: Despite progress, a 35 percentage point gap persists, representing approximately 230 million rural adults still outside the digital payment ecosystem.
Case Studies of Successful Financial Inclusion Initiatives in India
1. Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)
Overview:
- Launched in 2014 by the Government of India, PMJDY is one of the largest financial inclusion programs in the world. The scheme aimed to provide universal access to banking services, particularly for the unbanked population in rural and semi-urban areas.
Key Features:
- Zero-balance bank accounts with overdraft facilities (up to ₹10,000 for eligible customers).
- Rupay Debit Cards issued for digital transactions and ATM withdrawals.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) linkage for receiving government subsidies.
- Free accident insurance coverage of ₹2 lakh for RuPay cardholders.
- Encouragement of mobile banking and digital payments among new account holders.
Impact:
- Over 500 million accounts opened by August 2023, with total deposits exceeding ₹2 trillion.
- 55.5% of account holders are women, promoting financial empowerment.
- Rural and semi-urban participation increased significantly, with more people using formal banking channels.
- Enhanced financial literacy and accessibility to credit and insurance.
3. Unified Payments Interface (UPI) – Digital Financial Inclusion
Overview:
- UPI, launched by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) in 2016, revolutionized digital payments by enabling seamless, real-time transactions. It eliminated the need for physical bank visits or card-based payments, making financial transactions more inclusive.
Key Features:
- Instant, 24/7 fund transfers across banks using mobile phones.
- QR-code based transactions, reducing reliance on ATMs or PoS terminals.
- Small-value payments enable street vendors, small shopkeepers, and rural merchants to accept digital payments.
- Integration with government programs for seamless financial transactions.


Impact:
- Over 10 billion transactions per month (as of 2024), making India a global leader in digital payments.
- Rural and semi-urban digital transactions have surged, reducing dependence on cash.
- Empowered small businesses and informal sector workers by providing easy-to-use, secure digital payment options.
- Enhanced transparency and financial security through recorded transactions.
Barriers to Financial Inclusion
- Lack of Financial Literacy: Many individuals, especially in rural areas, lack awareness about banking services, credit options, and digital payments. This limits their ability to make informed financial decisions. Without financial education, people often rely on informal and high-cost financial services.
- Limited Banking Infrastructure: Many remote and underserved areas lack sufficient bank branches, ATMs, and financial service providers. Poor access to banking facilities forces people to depend on cash transactions and informal lending. Expanding digital and mobile banking is essential to bridging this gap.
- Low Digital and Technological Penetration: Limited smartphone access, poor internet connectivity, and lack of digital skills prevent people from using online banking and payment systems. Many rural populations still rely on cash due to unfamiliarity with digital tools. Strengthening digital infrastructure can boost financial inclusion.
- Income and Employment Instability: Many low-income individuals, particularly daily wage earners and informal workers, struggle to maintain regular banking activity. Irregular income patterns make it difficult for them to save, access credit, or use insurance services. Financial products tailored to unstable incomes can help address this issue.
Conclusion
Financial inclusion is a key driver of economic growth, poverty reduction, and social empowerment. By ensuring access to banking, credit, insurance, and digital payments, it enables individuals, especially in under served communities, to participate in the formal economy. Initiatives like PMJDY, UPI, and microfinance programs have significantly improved financial accessibility in India. However, challenges such as low financial literacy, inadequate banking infrastructure, and digital divide still hinder full inclusion. Addressing these barriers through financial education, digital expansion, and policy support will pave the way for a more inclusive and resilient financial ecosystem, fostering sustainable development for all.





