Prologue
- The global FinTech market reached $312.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at 17.5% CAGR to $882.3 billion by 2030, fueled by digital banking adoption.
- FinTech lenders now originate 38% of U.S. personal loans through faster, algorithm-driven approval processes.
- India’s FinTech sector is projected to hit $150 billion by 2025, growing at 22% CAGR. UPI has become the backbone of digital payments, processing over 14 billion monthly transactions.
Introduction
The financial technology (fintech) revolution is fundamentally reshaping the banking industry. By leveraging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, big data, and cloud computing, fintech firms are delivering financial services in ways that are faster, more efficient, and more customer-centric than traditional banks. This report explores the key areas where fintech is disrupting traditional banking models, the implications for legacy institutions, and the future of banking in a digital world.
This disruption is particularly evident in markets like India, where UPI-powered payments and digital lending platforms have gained massive adoption, forcing traditional banks to accelerate their digital transformation. As FinTech continues to bridge gaps in financial inclusion and redefine user expectations, the banking sector faces a critical inflection point—adapt to this tech-driven revolution or risk obsolescence. This exploration delves into the key drivers, impacts, and future trends of FinTech’s disruption, highlighting how it is reshaping the very foundations of traditional banking models.
What is Fintech?
FinTech (Financial Technology) refers to the innovative use of technology to deliver financial services more efficiently, affordably, and accessibly. It encompasses digital platforms, apps, and software that disrupt traditional banking by offering solutions like mobile payments, peer-to-peer lending, robo-advisory, blockchain-based transactions, and AI-driven financial tools.
By leveraging advancements such as artificial intelligence, big data, and cloud computing, FinTech companies streamline processes, reduce costs, and enhance customer experiences—catering to both underserved populations and tech-savvy consumers. From startups like PayPal and Stripe to embedded finance in e- commerce, FinTech is reshaping how money is managed, transferred, and invested worldwide.
Key Technologies Behind Fintech:
- Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
- Blockchain & Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
- Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)
- Biometric Authentication
- Cloud Computing & Data Analytics
Overview of Traditional Banking Models
Traditional banking models refer to the conventional system of financial intermediation where banks act as the primary link between depositors and borrowers. These models have long served as the foundation of the global financial system. Here’s an overview of their core structure and operations:
Deposit and Lending:
- Banks accept deposits (savings, current, fixed) and provide loans (personal, mortgage, business) at interest.
- Profit comes from the spread between lending and deposit rates (net interest margin).
Payment Systems:
- Facilitate transactions via checks, wire transfers, and card networks (Visa/Mastercard).
- Heavy reliance on physical branches and legacy systems (e.g., SWIFT for cross-border payments).
Wealth and Advisory Services:
- Offer investment products (FDs, mutual funds) and personalized financial advice through human advisors.
- High fees (1–2% of AUM) and minimum balance requirements exclude low-income users.
Regulatory Framework:
- Central banks (RBI, Fed) enforce capital reserves, KYC/AML norms, and deposit insurance (e.g., DICGC in India).
- Slow innovation due to compliance burdens and risk aversion.
Manual Loan Underwriting and Approvals:
- Credit decisions often involve paper-based documentation, human evaluation, and lengthy approval timelines.
Face-to-Face Customer Interactions:
- Most services are delivered through physical branches, requiring customers to visit in person for account setup, transactions, and support.
In-Branch Services for Most Transactions:
- Traditional banks prioritize branch-based operations, including deposits, withdrawals, loans, and customer service.
Key Areas Where Fintech is Disrupting Traditional Banking
Fintech (Financial Technology) is reshaping the financial services landscape by offering faster, cheaper, and more customer-centric solutions. It challenges the traditional banking model across several key areas:
Digital Payments:
Fintech has revolutionized payments through digital wallets, UPI, and contactless methods. Platforms like Google Pay and PhonePe offer instant, secure transactions without the need for cash or cards. This shift enhances convenience and promotes financial inclusion across all segments.
Digital Lending:
Fintech lenders use AI, big data, and alternative credit scoring to provide quick, paperless loans. Unlike traditional banks, they offer instant approvals and minimal documentation. This approach expands access to credit, especially for underserved individuals and small businesses.
Investment Platforms
Platforms like Zerodha, Groww, and Upstox have simplified investing through intuitive apps and low-cost trading. They provide access to stocks, mutual funds, and ETFs, even for first-time investors. Automation and robo-advisors further personalize investment strategies.
Neobanks:
Neobanks are fully digital banks that operate without physical branches, offering services via mobile apps. They provide seamless banking experiences with lower fees and real-time support. Their tech-first model appeals especially to younger, tech-savvy users.
Blockchain and DeFi:
Blockchain technology enables decentralized finance (DeFi), reducing reliance on traditional intermediaries. It supports peer-to-peer transactions, smart contracts, and transparent record-keeping. This innovation challenges the central control of financial systems and improves efficiency.
Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) Services:
BNPL services let customers split purchases into smaller, interest-free installments. Companies like Simpl and ZestMoney offer flexible credit at the point of sale, both online and offline. This model enhances affordability and boosts consumer spending.
Challenges Faced by Traditional Banks
Fintech has revolutionized payments through digital wallets, UPI, and contactless methods. Platforms like Google Pay and PhonePe offer instant, secure transactions without the need for cash or cards. This shift enhances convenience and promotes financial inclusion across all segments.
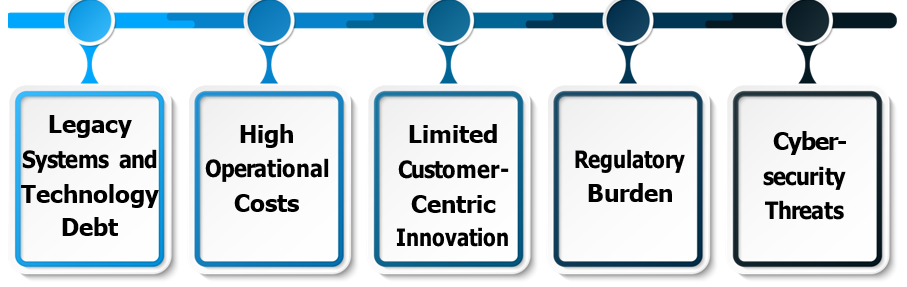
Traditional banks face significant challenges in adapting to the rapid evolution of financial services driven by FinTech innovation. Their legacy IT systems, often decades old, create technological inertia that makes digital transformation costly and complex, while stringent regulatory requirements further slow their ability to innovate. High operational costs from maintaining physical branches and large workforces put them at a competitive disadvantage against leaner FinTech firms that operate with greater efficiency and lower overheads.
Customer expectations have shifted dramatically toward seamless digital experiences, personalized services, and instant transactions—demands that traditional banks struggle to meet due to their bureaucratic structures and risk-averse cultures. Additionally, the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) and alternative lending platforms threatens their core revenue streams from interest margins and fees. Cybersecurity risks have also intensified as digital banking expands, requiring massive investments in protection measures.
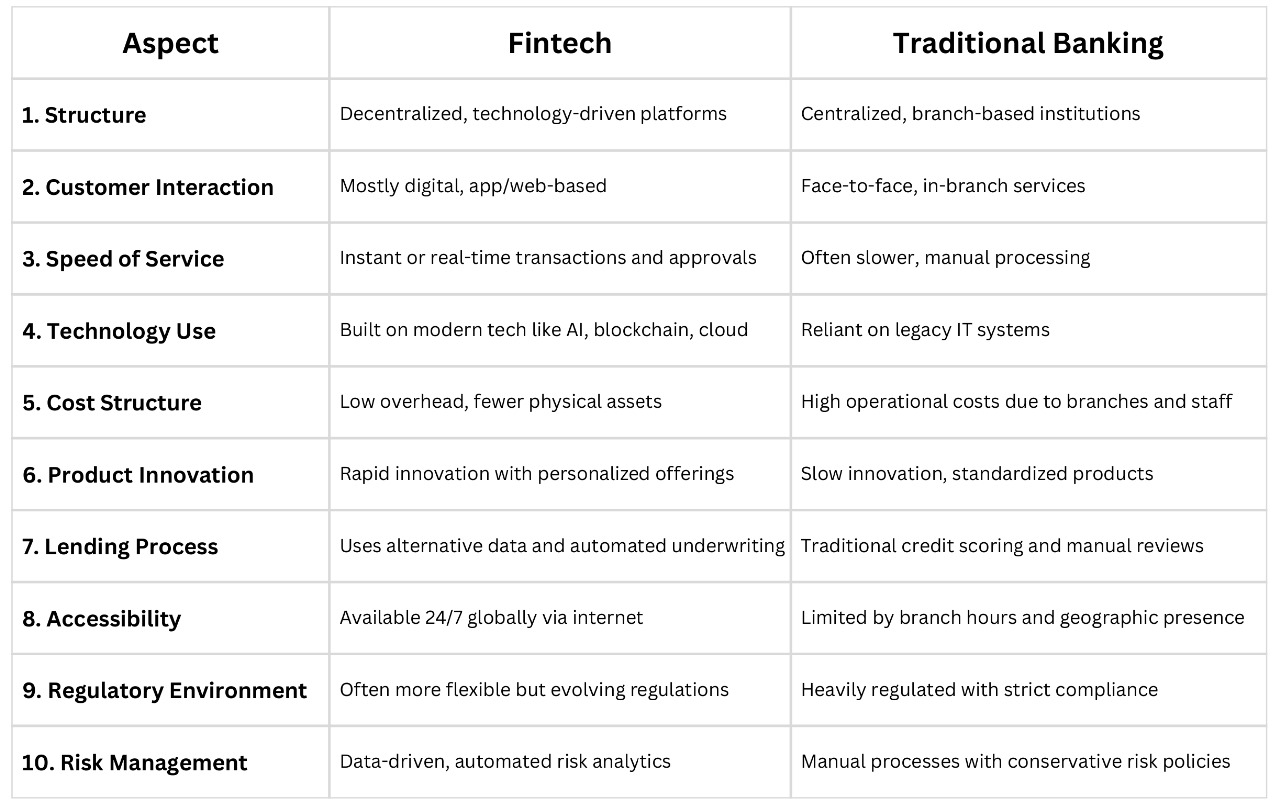
Fintech vs. Traditional Banking:
The financial industry is undergoing a significant transformation as fintech companies rapidly innovate and challenge the long-established traditional banking models. While traditional banks have historically dominated by offering comprehensive financial services through physical branches and legacy systems, fintech firms leverage cutting-edge technology to provide faster, more accessible, and customer-centric solutions. This shift is reshaping how individuals and businesses access financial products, forcing traditional banks to adapt or risk losing market share in an increasingly digital world.
How Traditional Banks are Responding
Traditional banks are actively adapting to the fintech disruption by embracing digital transformation and innovation. Many are investing heavily in upgrading legacy IT systems and developing user-friendly digital platforms to enhance customer experience. Overall, traditional banks aim to stay relevant by blending their established trust and scale with fintech agility and innovation.
Digital Transformation Initiatives:
Banks are upgrading their legacy systems and investing in mobile and online platforms to offer seamless digital experiences. This shift helps them meet customer expectations for convenience and speed. Many are accelerating their tech adoption to stay competitive in the digital age.
Partnerships and Acquisitions:
To leverage fintech innovations, banks are collaborating with or acquiring fintech startups. These partnerships enable banks to integrate new technologies quickly without building them from scratch. It also helps banks expand their product offerings and reach new customer segments.
Focus on Customer Experience:
Traditional banks are redesigning services to be more personalized and user-friendly by using data analytics and AI. Enhanced customer engagement through digital channels is a priority to retain and attract tech-savvy users. This approach helps banks compete with fintech’s customer-centric models.
Operational Efficiency and Automation:
Banks are automating manual processes such as loan approvals, KYC, and fraud detection to reduce costs and improve turnaround times. Automation enhances accuracy and allows staff to focus on higher-value tasks. This transformation improves overall operational agility.
Case Studies
Paytm – India’s Digital Financial Ecosystem
Overview:
Paytm revolutionized India’s cash-dominated economy by creating a mobile- first digital payments ecosystem. Starting as a prepaid recharge platform in 2010, it expanded into wallets, UPI, banking, and e-commerce, becoming a household name post-2016 demonetization.

Key Innovations & Impact:
- Mobile Wallets & QR Payments: Pioneered QR-based transactions for merchants, onboarding 20M+ small businesses.
- UPI Dominance: Processed 283.5 crore UPI transactions in December 2023, despite later regulatory challenges.
- Diversification: Launched Paytm Payments Bank (2017), insurance, and lending services, though regulatory non-compliance (e.g., KYC lapses) led to RBI restrictions in 2024.
JPMorgan Chase – In-House Fintech Innovation
Overview:
JPMorgan countered fintech disruption with a $17B tech budget (2024), blending acquisitions (e.g., OnDeck) with AI-driven internal innovation.

Key Innovations & Impact:
- AI & Automation:
- ChatCFO: An LLM for financial modeling saved 90% manual work in cash flow analysis 14.
- IndexGPT: AI-powered real-time investment advice boosted client engagement 14.
- Cloud Modernization: Migrated 80% of applications to cloud, enabling scalable APIs and fraud detection 14.
- Partnerships: Collaborated with OnDeck to streamline SME lending, cutting approval times by 70%.
Processed $10T daily with AI-driven KYC, handling 50% more files with 20% fewer employees 14.
Stock Performance: Maintained dominance with $600B+ market cap, outperforming peers in digital adoption.
Razorpay – SME Payment Solutions
Overview:
Razorpay emerged as a leader in India’s fintech space by simplifying payments for SMEs with APIs, automating payroll, and offering embedded finance solutions.

Key Innovations & Impact:
- Seamless Integration: Developer-friendly APIs enabled SMEs to embed payments into websites/apps, reducing reliance on legacy banking systems.
- Neobanking (RazorpayX): Provided automated business banking (e.g., vendor payments, tax compliance) with 50.5% CAGR growth projected by 2025.
- UPI & BNPL: Capitalized on India’s digital boom, processing $60B+ annual transactions
- Future Focus: Expanding into lending and international payments while navigating evolving RBI regulations.
Future of Banking
The future of banking is set to be defined by digital innovation, customer-centricity, and seamless integration of technology. Banks will increasingly adopt artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and data analytics to enhance decision-making, personalize services, and improve security. The rise of open banking will enable greater collaboration between banks, fintechs, and third-party providers, fostering an ecosystem that offers more tailored and diversified financial products.
Physical branches will evolve into advisory hubs, while most routine transactions shift to digital platforms accessible anytime, anywhere. Additionally, sustainability and ethical finance will gain prominence, as customers and regulators demand responsible banking practices. Overall, the future banking landscape will be agile, transparent, and highly responsive to evolving customer needs and global economic trends. The future belongs to agile, tech-driven financial ecosystems—where FinTechs lead innovation, but banks provide stability. Traditional players must accelerate digital transformation, or risk becoming obsolete.
Conclusion
- Fintech is fundamentally reshaping the banking industry by introducing innovative, technology-driven solutions that prioritize speed, convenience, and customer experience.
- By leveraging digital platforms, data analytics, and automation, fintech firms have challenged the limitations of traditional banks, such as legacy systems, high costs, and slow processes.
- This disruption is driving a shift toward more inclusive, accessible, and personalized financial services.
- To stay competitive, traditional banks must embrace digital transformation, collaborate with fintech players, and rethink their business models.
- This shift is reshaping how individuals and businesses access financial products, forcing traditional banks to adapt or risk losing market share in an increasingly digital world.
- Ultimately, the fusion of fintech innovation with traditional banking strengths promises a more efficient, transparent, and customer-centric financial ecosystem.





